When it comes to securing a mortgage, credit score directly impacts your mortgage interest rates and plays a pivotal role in determining the interest rate you’ll receive. A higher credit score can lead to lower mortgage rates, which can save you thousands of dollars over the life of your loan. In this article, we’ll explore the basics of credit scores, how mortgage rates are computed, and the ways your credit score can impact your mortgage rate.
Basics of Your Credit Score
A credit score is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness, typically ranging from 300 to 850. It is calculated based on several factors, including your payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, types of credit accounts, and recent credit inquiries. The most commonly used credit scoring models are FICO and VantageScore, both of which weigh these factors differently.
- Payment History (35%): This is the most significant factor. It reflects whether you’ve paid your bills on time.
- Credit Utilization (30%): This measures how much of your available credit you’re using. Lower utilization rates are better.
- Length of Credit History (15%): A longer credit history can positively impact your score.
- Types of Credit (10%): A mix of credit types (credit cards, installment loans, etc.) can be beneficial.
- New Credit Inquiries (10%): Too many inquiries in a short period can negatively affect your score.
Understanding these components can help you manage your credit more effectively.
How Your Mortgage APR is Computed
The Annual Percentage Rate (APR) on your mortgage is a broader measure of the cost of borrowing. It includes not only the interest rate but also any fees or additional costs associated with the loan. Lenders use your credit score, along with other factors such as loan amount, down payment, and loan type, to determine your APR. At the same time, the higher your credit score, the lower the risk that you’ll default on your mortgage loan, and the lower the interest rate you’ll qualify for.
The formula for calculating APR is complex, but it essentially takes into account the total cost of the loan over its term, expressed as a yearly rate. A lower credit score typically results in a higher APR, as lenders perceive you as a higher risk. The chart below illustrates the relationship between credit scores and interest rates, and how one impacts the other:
The Relationship between Credit Scores and Interest Rates
For a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage of $200,000, a good credit score would give you a low interest rate, saving you tens of thousands of dollars in interest over the course of the loan.
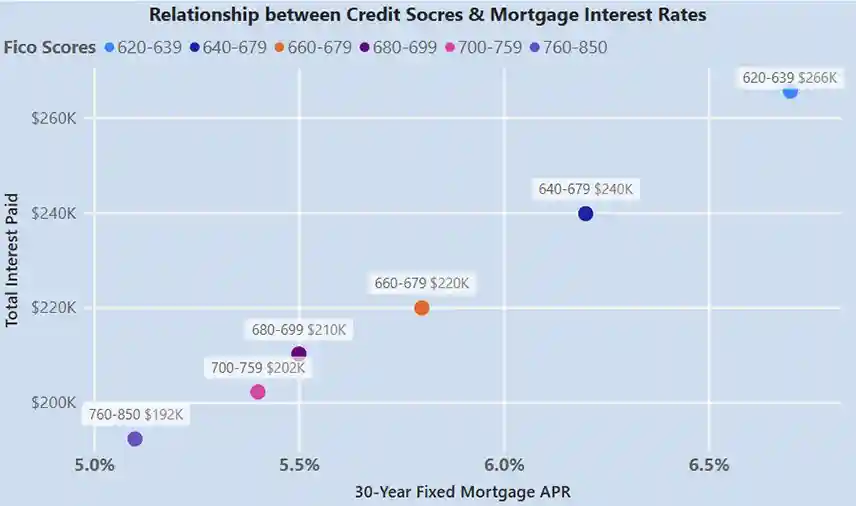
How Credit Scores Can Affect Your Mortgage Rate
Your credit score directly influences the interest rate you’ll be offered on your mortgage. Generally, the higher your score, the lower your interest rate will be. For example, a borrower with a credit score of 760 or higher may qualify for the best rates, while someone with a score below 620 may face significantly higher rates or even difficulty securing a loan.
Lenders use tiered pricing models, where different credit score ranges correspond to different interest rates. A small difference in your credit score can lead to a substantial difference in your monthly payments and the total cost of your mortgage.
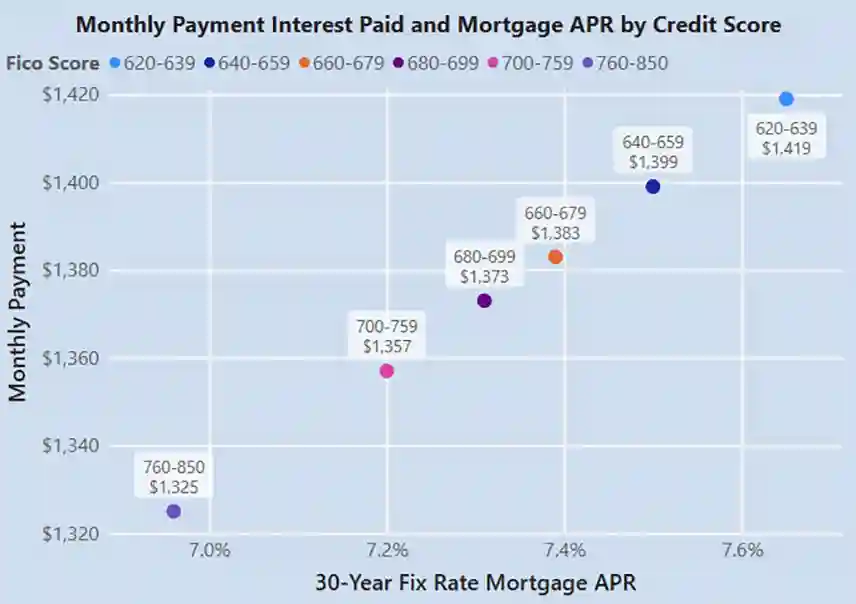
A loan savings calculator, such as the one offered by myFICO, can demonstrate the impact of credit scores on mortgage rates. Take an example of $200,000 principal loan amount on a 30-year fixed rate will show mortgage APR rates, monthly payment, and interest paid as (current as of March 2024):
- 760 to 850: APR of 6.96% with a monthly payment of $1,325. The total interest paid on the mortgage would be $276,892.
- 700 to 759: APR of 7.20% with a monthly payment of $1,357. The total interest paid on the mortgage would be $288,484.
- 680 to 699: APR of 7.31% with a monthly payment of $1,373. The total interest paid on the mortgage would be $294,296.
- 660 to 679: APR of 7.39% with a monthly payment of $1,383. The total interest paid on the mortgage would be $297,777.
- 640 to 659: APR of 7.50% with a monthly payment of $1,399. The total interest paid on the mortgage would be $303,484.
- 620 to 639: APR of 7.65% with a monthly payment of $1,419. The total interest paid on the mortgage would be $310,900.
How Credit Scores are Used by Mortgage Lenders in the United States
In the United States, mortgage lenders rely heavily on credit scores to assess the risk of lending to a borrower. When you apply for a mortgage, lenders will pull your credit report from one or more of the major credit bureaus (Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax). They will evaluate your credit score and history to determine your eligibility for a loan and the terms of that loan.
Lenders may also consider other factors, such as your income, employment history, and debt-to-income ratio, but your credit score is often the most critical factor in determining your mortgage rate.
What Credit Score is Considered Best to Get the Best Mortgage Rates
To secure the best mortgage rates, a credit score of 760 or higher is generally considered ideal. Borrowers in this range are seen as low-risk, which allows lenders to offer them the most favorable terms. However, scores in the 700-759 range can still qualify for competitive rates, while scores below 620 may struggle to find lenders willing to offer a mortgage at all.
It’s essential to check your credit score before applying for a mortgage so you can take steps to improve it if necessary.
How Your Credit Score Could Save You Money on Your Mortgage
A higher credit score can lead to significant savings over the life of your mortgage. For example, a 1% difference in interest rates can result in thousands of dollars in additional interest payments. By improving your credit score, you can potentially save money on monthly payments and overall loan costs.
Example of Savings:
- Loan Amount: $300,000
- Interest Rate (3.0%): Monthly Payment = $1,264
- Interest Rate (4.0%): Monthly Payment = $1,432
The difference of $168 per month can add up to over $60,000 in interest over a 30-year mortgage.
Additionally, a lower interest rate can also reduce your monthly payment, making homeownership more affordable.
5 Ways to Raise Your Credit Score
Improving your credit score takes time, but there are several strategies you can employ:
- Pay Your Bills on Time: Consistently making payments on time is crucial for maintaining a good credit score.
- Reduce Credit Card Balances: Aim to keep your credit utilization below 30% of your total available credit.
- Avoid Opening New Credit Accounts: Each new inquiry can temporarily lower your score, so only apply for credit when necessary.
- Check Your Credit Report for Errors: Regularly review your credit report for inaccuracies and dispute any errors you find.
- Keep Old Accounts Open: The length of your credit history matters, so keep older accounts active even if you don’t use them frequently.
Summary
Your credit score is a vital factor in determining your mortgage rate. Understanding how it works and taking steps to improve it can save you money and make homeownership more accessible. By maintaining a good credit score, you can secure lower interest rates, which translates to significant savings over the life of your mortgage.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a good credit score for a mortgage?
A good credit score for a mortgage is typically considered to be 760 or higher.
2. How can I check my credit score?
You can check your credit score through various online services, credit card companies, or by requesting a free report from the major credit bureaus.
3. How long does it take to improve my credit score?
Improving your credit score can take time, often several months, depending on your current score and the actions you take.
4. Can I get a mortgage with a low credit score?
Yes, but you may face higher interest rates and stricter terms. Some lenders specialize in loans for borrowers with lower credit scores.
5. How often should I check my credit report?
It’s advisable to check your credit report at least once a year to ensure accuracy and monitor for any changes.
